范例代码(Mac下)
以一段Git代码提交脚本为例:
1 # 添加目录下所有文件
2 git add .
3 # message为git commit的值,默认值为当前时间,``间包含字符串将被按照命令执行。
4 message=`date +%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M`
5 # getopts命令可获取输入的参数,如m:则表示检查'-m'的参数输入,并将参数名存入opt中。
6 # 如果未找到参数,则存入?,参数值通过OPTARG变量获得,变量通过$取值。
7
8 while getopts m: opt
9 do
10 case $opt in
11 m)
12 message=$OPTARG
13 ;;
14 ?)
15 echo "Usage: args [-m]"
16 echo "-m means message"
17 echo "exit"
18 exit
19 ;;
20 esac
21 done
22 # git提交message信息
23 git commit -m "$message"
24 git push origin gh-pages
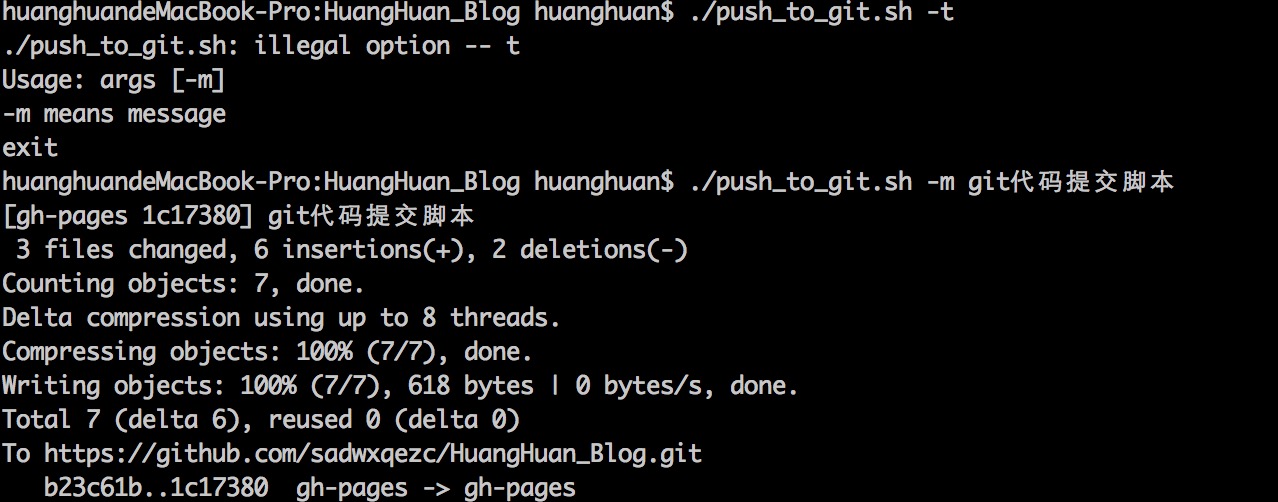
Git代码提交脚本执行效果截图:
基本知识介绍
一般所指的Shell是指Shell脚本(Shell script),是为Shell编写的脚本程序。而Shell本身是用户访问操作系统内核服务的程序界面,Shell编程与其它语言类似,只需要编写代码的编辑器和能够解释执行的程序即可。Bourne shell是标准的Shell解释器,其所在路径往往是/bin/sh。
在Shell脚本中,第一行一般是#!/bin/sh,#!是用于约定的标记,告诉系统该脚本需要什么解释器执行。当然如果文件以.sh作为后缀的话,不写这一行也能正确执行。
基本语法
Shell变量
- 变量定义与赋值
testVar="testValue" - 变量的取值只需要在前面加入
$符号,如$testVar,加花括号可以帮助解释器识别边界,如${testVar}
代码范例:
1 #! /bin/sh
2 count=0
3 for testVar in Let us learn Shell
4 do
5 echo "Word:${testVar}_Number:$count"
6 ((count++))
7 done
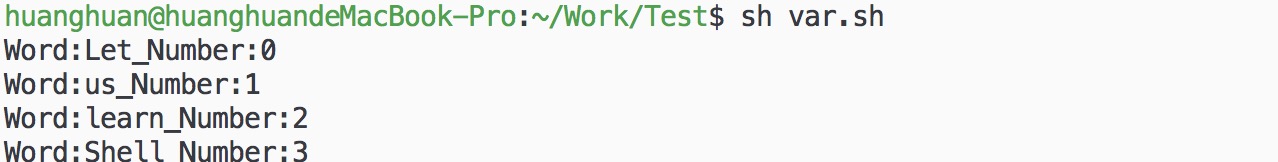
脚本执行结果:
字符串
- 单引号的特点:
1.单引号中的所有字符串都原样输出,字符串中的变量无效
2.单引号中不能出现单引号,转义亦无效 - 双引号的特点:
1.双引号中可以有变量,并读取变量值
2.双引号中可以出现转义字符 - ``符号之间字符串可用于执行指令
代码范例:
1 #! /bin/sh
2 testString='this is a test'
3 echo '$testString'
4 echo "$testString"
5 testString="${testString} string catenate"
6 echo $testString
7 testString=""$testString" string catenate"
8 echo $testString
9 echo "The length: ${#testString}"
10 echo "Part of the string: ${testString:1:7}"
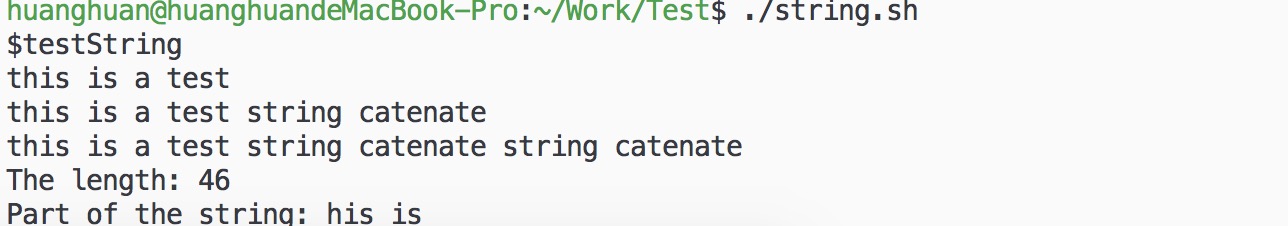
脚本执行结果:
Shell中的各种括号
作为脚本语言,shell各种各样的符号括号挺让人头疼,降低了其代码的可读性 参考:Shell中各种括号的作用
- Shell中大括号
{}可以用来限定变量名称的范围 - Shell中
``和(),可以执行其中的命令并读出结果 (())中支持POSIX标准的计算,符合C语言的运算符都可以用在其中,表达式真值为1,假则为0[]中放置条件表达式
代码范例:
1 #! /bin/sh
2 if ((1))
3 then
4 echo $(pwd)
5 fi
脚本执行结果:

条件判断与流程控制
if else代码范例:
1 if condition
2 then
3 phase one
4 phase two
5 elif condition2
6 then
7 phase three
8 else
9 #else后不能为空
10 phase four
1 fi
for while代码范例:
# for (shell)
1 for param in paramOne paramTwo ... paramN
2 do
3 phase one
4 phase two
5 done
# for (C)
1 for (( EXP1;EXP2;EXP3))
2 do
3 phase one
4 phase two
5 done
# while
1 while condition
2 do
3 phase one
4 done
case 代码范例:
1 case $opt in
2 valueOne)
3 phase one
4 ;;
5 valueTwo)
6 phase two
7 ;;
8 *)
9 echo "error"
10 esac
Shell函数
代码范例:
1 #! /bin/sh
2
3 function add(){
4 if [ $# != 2 ]
5 then
6 return 1
7 else
8 return $(($1+$2))
9 fi
10 }
11
12 add 1 2
13 echo "1+2=$?"
执行结果:

Shell传入变量
$0当前脚本的文件名$n第n个参数的值$#传入的参数个数$*所有参数$?上个命令的退出状态或行数的返回值$$当前Shell进行ID
Shell文件判断逻辑
-a或-e:文件是否存在-b:文件存在且为块特殊文件-c:文件存在且为字符特殊文件-d:文件存在且为一个目录-f:文件存在且为常规文件-L:文件存在且软链接-s:文件存在且不为空-r:文件存在且当前进程可读-w:文件存在且当前进程可写-x:文件存在且当前进程可执行-n:字符串长度不为空-z:字符串长度为空